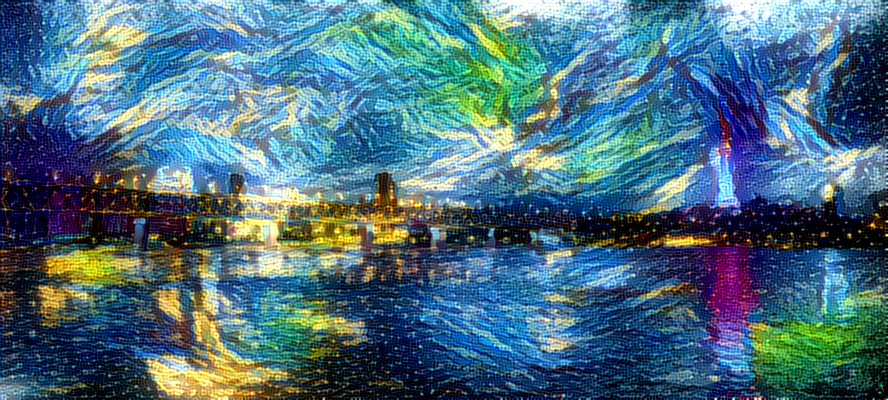
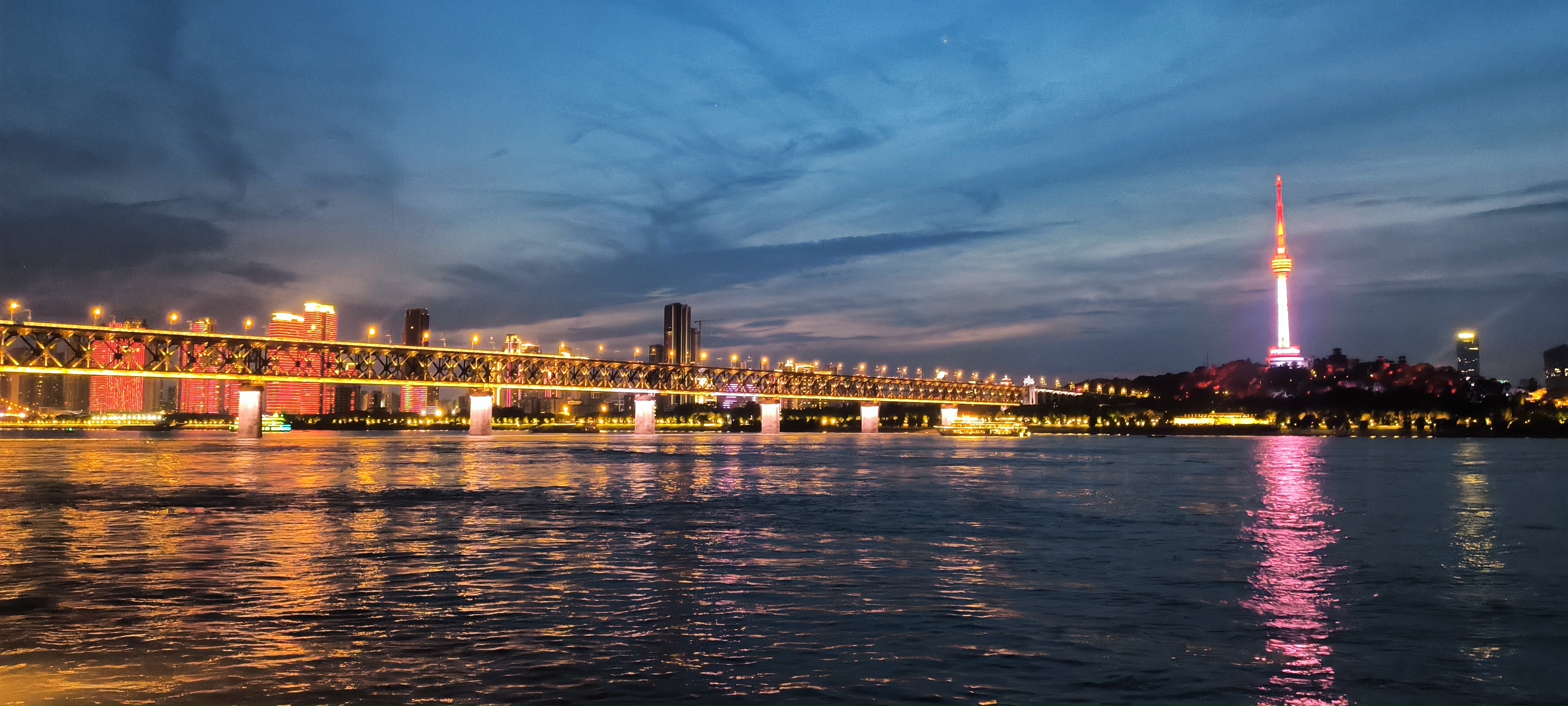
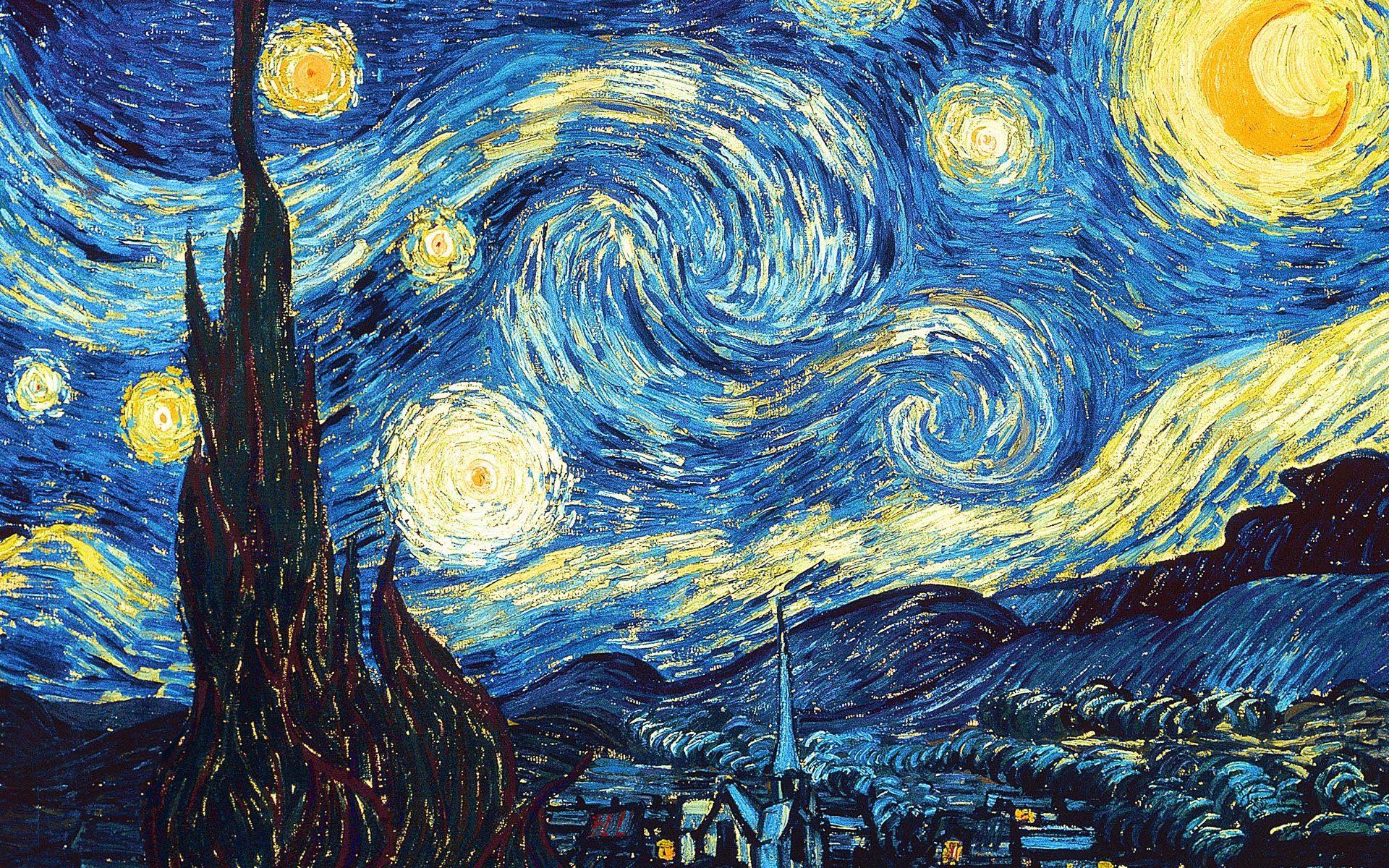
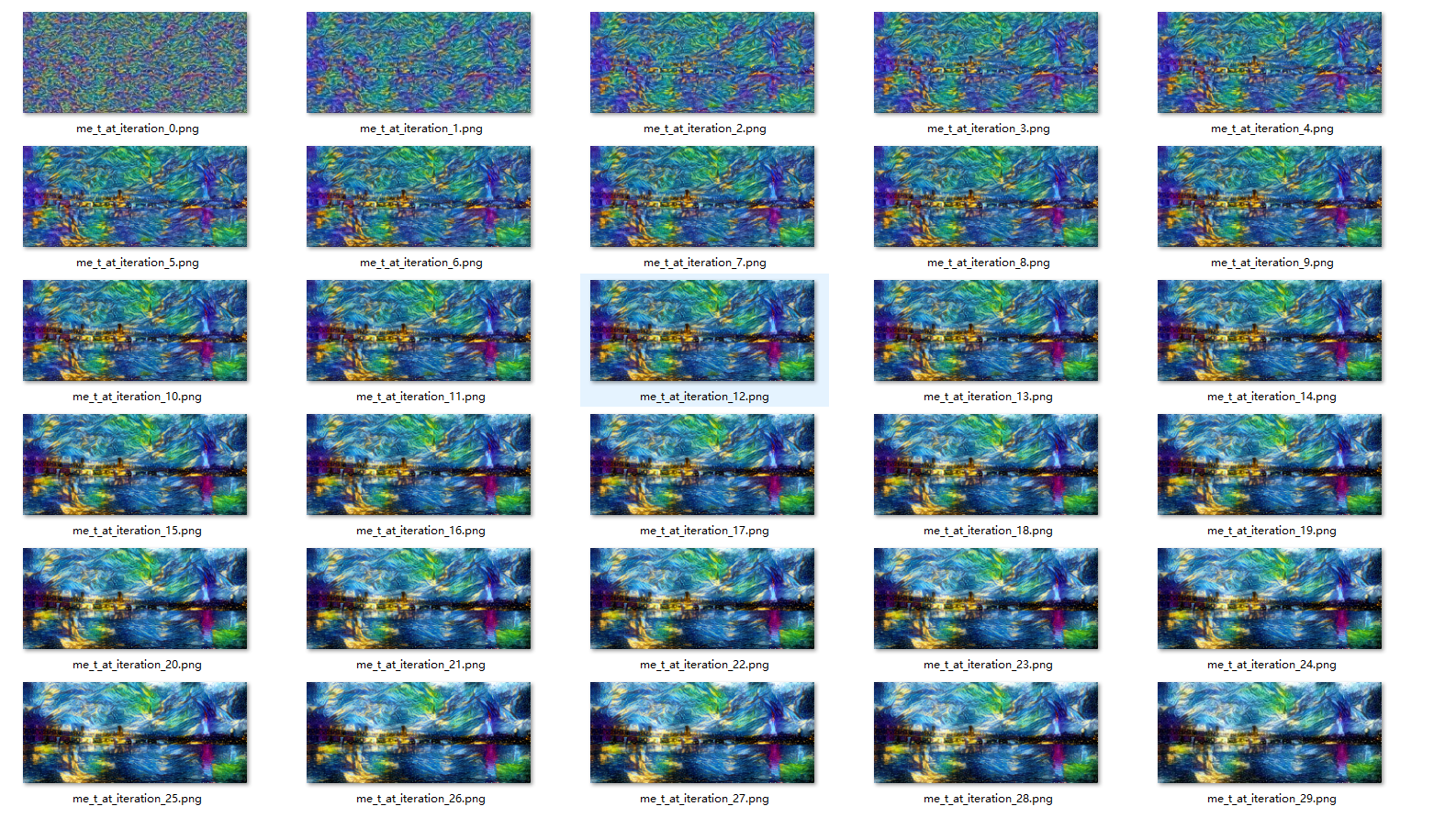
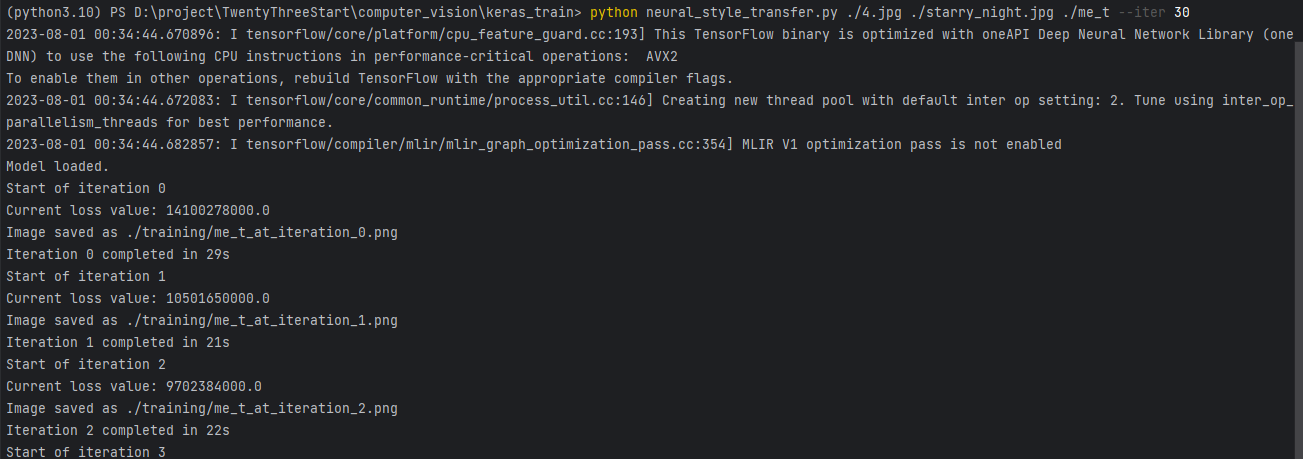
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
| from __future__ import print_function
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
import imageio
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import fmin_l_bfgs_b
import time
import argparse
from keras.applications import vgg16
from keras import backend as K
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK']='True'
import tensorflow as tf
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Neural style transfer with Keras.')
parser.add_argument('base_image_path', metavar='base', type=str,
help='Path to the image to transform.')
parser.add_argument('style_reference_image_path', metavar='ref', type=str,
help='Path to the style reference image.')
parser.add_argument('result_prefix', metavar='res_prefix', type=str,
help='Prefix for the saved results.')
parser.add_argument('--iter', type=int, default=10, required=False,
help='Number of iterations to run.')
parser.add_argument('--content_weight', type=float, default=0.025, required=False,
help='Content weight.')
parser.add_argument('--style_weight', type=float, default=1.0, required=False,
help='Style weight.')
parser.add_argument('--tv_weight', type=float, default=1.0, required=False,
help='Total Variation weight.')
args = parser.parse_args()
base_image_path = args.base_image_path
style_reference_image_path = args.style_reference_image_path
result_prefix = './training/' + args.result_prefix.split('/')[1]
iterations = args.iter
total_variation_weight = args.tv_weight
style_weight = args.style_weight
content_weight = args.content_weight
width, height = load_img(base_image_path).size
img_nrows = 400
img_ncols = int(width * img_nrows / height)
def preprocess_image(image_path):
img = load_img(image_path, target_size=(img_nrows, img_ncols))
img = img_to_array(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = vgg16.preprocess_input(img)
return img
def deprocess_image(x):
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x = x.reshape((3, img_nrows, img_ncols))
x = x.transpose((1, 2, 0))
else:
x = x.reshape((img_nrows, img_ncols, 3))
x[:, :, 0] += 103.939
x[:, :, 1] += 116.779
x[:, :, 2] += 123.68
x = x[:, :, ::-1]
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
return x
base_image = K.variable(preprocess_image(base_image_path))
style_reference_image = K.variable(preprocess_image(style_reference_image_path))
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
combination_image = K.placeholder((1, 3, img_nrows, img_ncols))
else:
combination_image = K.placeholder((1, img_nrows, img_ncols, 3))
input_tensor = K.concatenate([base_image,
style_reference_image,
combination_image], axis=0)
model = vgg16.VGG16(input_tensor=input_tensor,
weights='imagenet', include_top=False)
print('Model loaded.')
outputs_dict = dict([(layer.name, layer.output) for layer in model.layers])
def gram_matrix(x):
assert K.ndim(x) == 3
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
features = K.batch_flatten(x)
else:
features = K.batch_flatten(K.permute_dimensions(x, (2, 0, 1)))
gram = K.dot(features, K.transpose(features))
return gram
def style_loss(style, combination):
assert K.ndim(style) == 3
assert K.ndim(combination) == 3
S = gram_matrix(style)
C = gram_matrix(combination)
channels = 3
size = img_nrows * img_ncols
return K.sum(K.square(S - C)) / (4. * (channels ** 2) * (size ** 2))
def content_loss(base, combination):
return K.sum(K.square(combination - base))
def total_variation_loss(x):
assert K.ndim(x) == 4
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
a = K.square(x[:, :, :img_nrows - 1, :img_ncols - 1] - x[:, :, 1:, :img_ncols - 1])
b = K.square(x[:, :, :img_nrows - 1, :img_ncols - 1] - x[:, :, :img_nrows - 1, 1:])
else:
a = K.square(x[:, :img_nrows - 1, :img_ncols - 1, :] - x[:, 1:, :img_ncols - 1, :])
b = K.square(x[:, :img_nrows - 1, :img_ncols - 1, :] - x[:, :img_nrows - 1, 1:, :])
return K.sum(K.pow(a + b, 1.25))
loss = K.variable(0.)
layer_features = outputs_dict['block4_conv2']
base_image_features = layer_features[0, :, :, :]
combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :]
loss = loss + content_weight * content_loss(base_image_features,
combination_features)
feature_layers = ['block1_conv1', 'block2_conv1',
'block3_conv1', 'block4_conv1',
'block5_conv1']
for layer_name in feature_layers:
layer_features = outputs_dict[layer_name]
style_reference_features = layer_features[1, :, :, :]
combination_features = layer_features[2, :, :, :]
sl = style_loss(style_reference_features, combination_features)
loss += (style_weight / len(feature_layers)) * sl
loss += total_variation_weight * total_variation_loss(combination_image)
grads = K.gradients(loss, combination_image)
outputs = [loss]
if isinstance(grads, (list, tuple)):
outputs += grads
else:
outputs.append(grads)
f_outputs = K.function([combination_image], outputs)
def eval_loss_and_grads(x):
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x = x.reshape((1, 3, img_nrows, img_ncols))
else:
x = x.reshape((1, img_nrows, img_ncols, 3))
outs = f_outputs([x])
loss_value = outs[0]
if len(outs[1:]) == 1:
grad_values = outs[1].flatten().astype('float64')
else:
grad_values = np.array(outs[1:]).flatten().astype('float64')
return loss_value, grad_values
class Evaluator(object):
def __init__(self):
self.loss_value = None
self.grads_values = None
def loss(self, x):
assert self.loss_value is None
loss_value, grad_values = eval_loss_and_grads(x)
self.loss_value = loss_value
self.grad_values = grad_values
return self.loss_value
def grads(self, x):
assert self.loss_value is not None
grad_values = np.copy(self.grad_values)
self.loss_value = None
self.grad_values = None
return grad_values
evaluator = Evaluator()
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x = np.random.uniform(0, 255, (1, 3, img_nrows, img_ncols)) - 128.
else:
x = np.random.uniform(0, 255, (1, img_nrows, img_ncols, 3)) - 128.
for i in range(iterations):
print('Start of iteration', i)
start_time = time.time()
x, min_val, info = fmin_l_bfgs_b(evaluator.loss, x.flatten(),
fprime=evaluator.grads, maxfun=20)
print('Current loss value:', min_val)
img = deprocess_image(x.copy())
fname = result_prefix + '_at_iteration_%d.png' % i
imageio.imwrite(fname, img)
end_time = time.time()
print('Image saved as', fname)
print('Iteration %d completed in %ds' % (i, end_time - start_time))
|